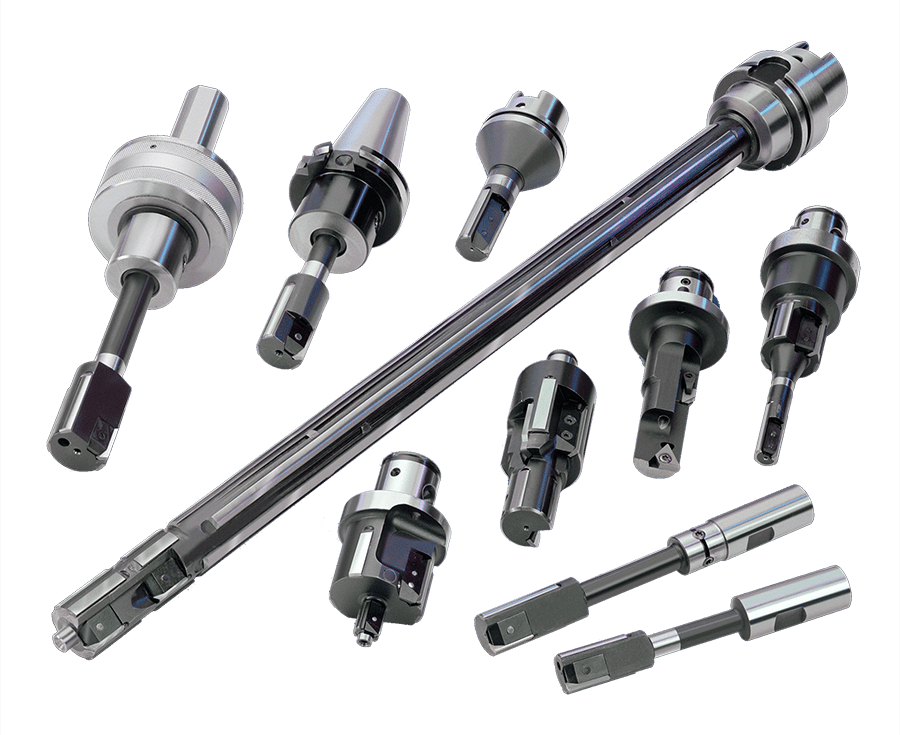
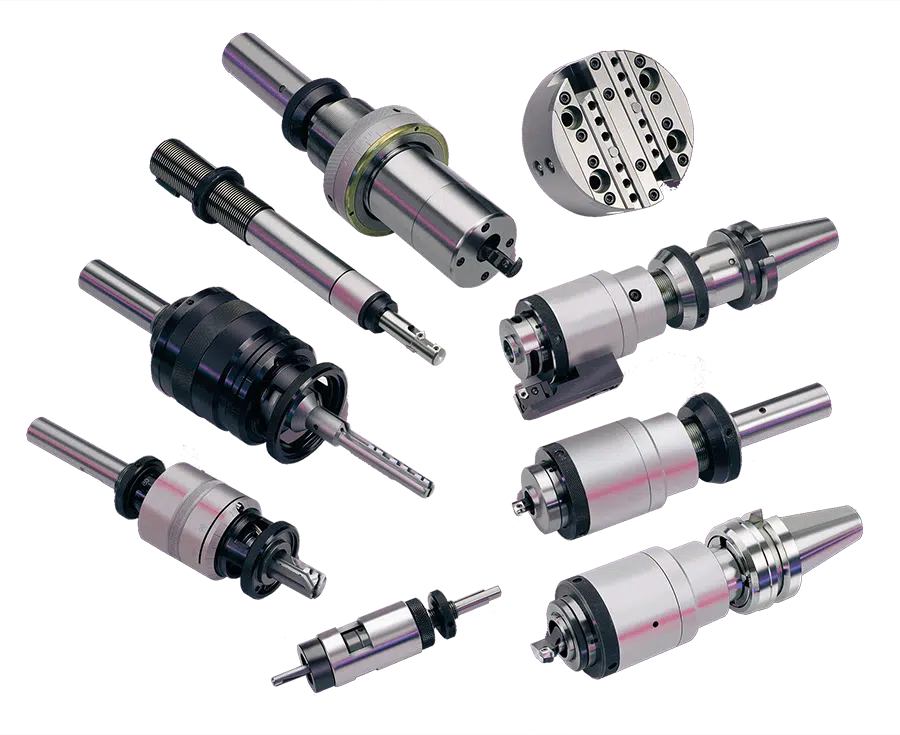
Cogsdill Thread Root Rolling Tools (TRR), also known as cold root rolling, significantly increase the fatigue strength of highly stressed components whilst also producing a superior surface finish. Together these reduce the chance of corrosion and dramatically extend the life of threaded connections.
ROLLING IN THE DEEP
ROLLING IN THE DEEP
Cold Root Rolling is an advanced method of roller burnishing that uses controlled pressure to cold-form the material at the root of newly machined or previously cut threads.
This process introduces a compressive residual stress that cancels out the tensile stress that the component is subjected to during use.
Cold Root Rolling is an advanced method of roller burnishing that uses controlled pressure to cold-form the material at the root of of newly machined or previously cut threads.
This process introduces a compressive residual stress that cancels out the tensile stress that the component is subjected to during use.

Plastic deformation
Plastic deformation
Using a hardened formed HSS roll that matches both the profile and designated radius of the tapered thread, pressure is applied in order to deeply penetrate the root radius, which displaces and deforms the thread material.
Using a hardened formed HSS roll that matches both the profile and designated radius of the tapered thread, pressure is applied in order to deeply penetrate the root radius, which displaces and deforms the thread material.
Drill String Connectors
Oil & Gas
The most common reason for failure is fatigue wear at the pipe thread. This is due to the drill string repeatedly bending when directional drilling – potentially over several kilometres and at angles up to 90 degrees. The repeated cyclic stress of compression and tension can cause the material to crack and fracture.
As a preventative solution, Cold Root Rolling ensures extended wear life to the pipe thread connection by altering the materials substructure and improving the surface finish to diminish corrosion that occurs in harsh environments.
Drill String Connectors
Oil & Gas
The most common reason for failure is fatigue wear at the pipe thread. This is due to the drill string repeatedly bending when directional drilling – potentially over several kilometres and at angles up to 90 degrees. The repeated cyclic stress of compression and tension can cause the material to crack and fracture.
As a preventative solution, Cold Root Rolling ensures extended wear life to the pipe thread connection by altering the materials substructure and improving the surface finish to diminish corrosion that occurs in harsh environments.
Controlled cold rolling
Controlled cold rolling
| 1 | The rolling force is provided by a pre-loaded spring. |
| 2 | The tool is fed radially into the workpiece by a specified amount depending on the size of the connector being rolled. |
| 3 | The tool is then fed up the threads using the thread re-cut cycle on the machine. |
| 4 | This deforms the root of the thread and introduces the compressive residual stress. |
| 1 | The rolling force is provided by a pre-loaded spring. |
| 2 | The tool is fed radially into the workpiece by a specified amount depending on the size of the connector being rolled. |
| 3 | The tool is then fed up the threads using the thread re-cut cycle on the machine. |
| 4 | This deforms the root of the thread and introduces the compressive residual stress. |
Reduce pipe failure
Reduce downtime
Reduce costs
Reduce pipe failure
Reduce downtime
Reduce costs




Box & Pin
Two types of Thread Root Rolling Tools (TRR) are available.
- TRR-IN (Box) for internal (female) threads
- TRR-EX (Pin) for external (male) threads
Both are available in multiple shank options with various roll radii to suit your thread requirements.
Box & Pin
Two types of Thread Root Rolling Tools (TRR) are available.
- TRR-IN (Box) for internal (female) threads
- TRR-EX (Pin) for external (male) threads
Both are available in multiple shank options with various roll radii to suit your thread requirements.







Increase strength. Reduce failures.
Whilst diminishing corrosion and fatigue wear of highly stressed components.








Standard Tool Specifications

TRR-EX (PIN)
| Thread Sizes | Shank Options |
| NC38 to NC61 | Capto C6 |
| HSK 63 | |
| 3 1/2 reg to 7 5/8 reg | 25mm sq. |
| 32mm sq. | |
TRR-IN (BOX)
| Thread Sizes | Shank Options |
| NC38 to NC70 | |
| Capto C6 | |
| 3 1/2 reg to 7 5/8 reg | HSK 63 |
| Ø50mm | |
Technical Data
| Connection Size | Thread form | Thread root radius (in) | Roller Diameter (in) | Roller Edge Radius (in) | Required Roller Force (lbf) | Required Roller Force (lbf) | Required Roller Force (lbf) | Required Roller Force (kN) |
| Number (NC) Style | BOX | PIN | ||||||
| NC38 | V-0.0038R | 0.038 | 0.787 | 0.042 | 2925 | 13 | 1800 | 8 |
| NC40 | V-0.0038R | 0.038 | 0.787 | 0.042 | 2925 | 13 | 1800 | 8 |
| NC44 | V-0.0038R | 0.038 | 0.787 | 0.042 | 2700 | 12 | 1800 | 8 |
| NC46 | V-0.0038R | 0.038 | 0.787 | 0.042 | 2700 | 12 | 2025 | 9 |
| NC50 | V-0.0038R | 0.038 | 0.787 | 0.042 | 2700 | 12 | 2025 | 9 |
| NC56 | V-0.0038R | 0.038 | 0.787 | 0.042 | 2700 | 12 | 2025 | 9 |
| NC61 | V-0.0038R | 0.038 | 0.787 | 0.042 | 2475 | 11 | 2025 | 9 |
| Regular (Reg) Style | ||||||||
| 3 1/2 | V-0.040 | 0.02 | 0.787 | 0.022 | 1575 | 7 | 900 | 4 |
| 4 1/2 | V-0.040 | 0.02 | 0.787 | 0.022 | 1350 | 6 | 900 | 4 |
| 5 1/2 | V-0.050 | 0.025 | 0.787 | 0.027 | 1800 | 8 | 1350 | 6 |
| 6 5/8 | V-0.050 | 0.025 | 0.787 | 0.027 | 1800 | 8 | 1350 | 6 |
| 7 5/8 | V-0.050 | 0.025 | 0.787 | 0.027 | 1575 | 7 | 1350 | 6 |
|
Typical Speed: |
30 RPM |
|
|
Feed: |
Same as threading (use thread re-cut cycle) |
|
|
Interference: |
Dependent on connection size and type |
|
|
Nominal Pre Load: |
8.33 kN |
|
|
Deflection Load: |
0.155 kN per 0.01mm |
|
|
Example: |
NC38 BOX requires 13 kN force |